Reading Time: 7 minutesAccidentally wiping a hard drive can result in the loss of valuable data, leaving many users wondering if recovery is possible. The good news is that it is often possible to recover data from a wiped hard drive, especially if you act quickly. In this article, we’ll show you how to recover a wiped hard drive on a Windows computer using three different methods.
Methods to Recover Wiped Hard Drive on Windows
When it comes to recovering data from a wiped hard drive, there are three primary methods you can consider. The first and most straightforward option is to restore data from an available backup. If you’re using OneDrive to backup important files to the cloud, relying on the File History feature to create incremental backups on another storage device, or manually backing up important files, you may be able to recover your data without any additional tools or services.
However, if you don’t have a backup or it’s outdated, the next best option is to use data recovery software. These programs can scan the wiped hard drive and recover data that hasn’t been overwritten with new data. The best data recovery software can even recover file metadata and folder structures, making it easy to get back to work after a wiping disaster.
If data recovery software doesn’t yield any results, you can always consider professional data recovery services. The experts employed by these services have access to professional-grade data recovery software and hardware tools, so there’s a chance they’ll be able to deliver results even if DIY recovery attempts were unsuccessful. They can also repair any physical damage that’s making the hard drive inaccessible. However, professional data recovery services can be expensive, so it’s important to weigh the cost against the value of the data you’re trying to recover.
How to Increase Chances for Data Recovery
The success of your data recovery procedure depends on various factors such as–the reason for data loss, time elapsed, and whether you used the drive after data loss. To substantially increase the extent of data recovery, keep the following tips in mind:
- Stop using the drive as soon as you discover the data loss. Writing new data to the drive overwrites the previous data and makes it irrecoverable. Even the normal operations of Windows can write new files to the drive.
- Attempt data recovery as soon as possible. Delaying data recovery increases the chances of new data being written to the drive.
- Use the best data recovery program right from the beginning. The first data recovery attempt is the most successful.
- Save the recovered files on another drive to prevent overwriting of data or chances of deletion again.
- Contact a data recovery service if the drive was wiped because of physical damage. Don’t tamper with the drive at home.
Option 1: Recover Data from an Available Backup
If you have previously created backups of your important files and data, then it is possible to recover your wiped hard drive from them. Here are the steps to recover data from three common Windows backup methods:
OneDrive:
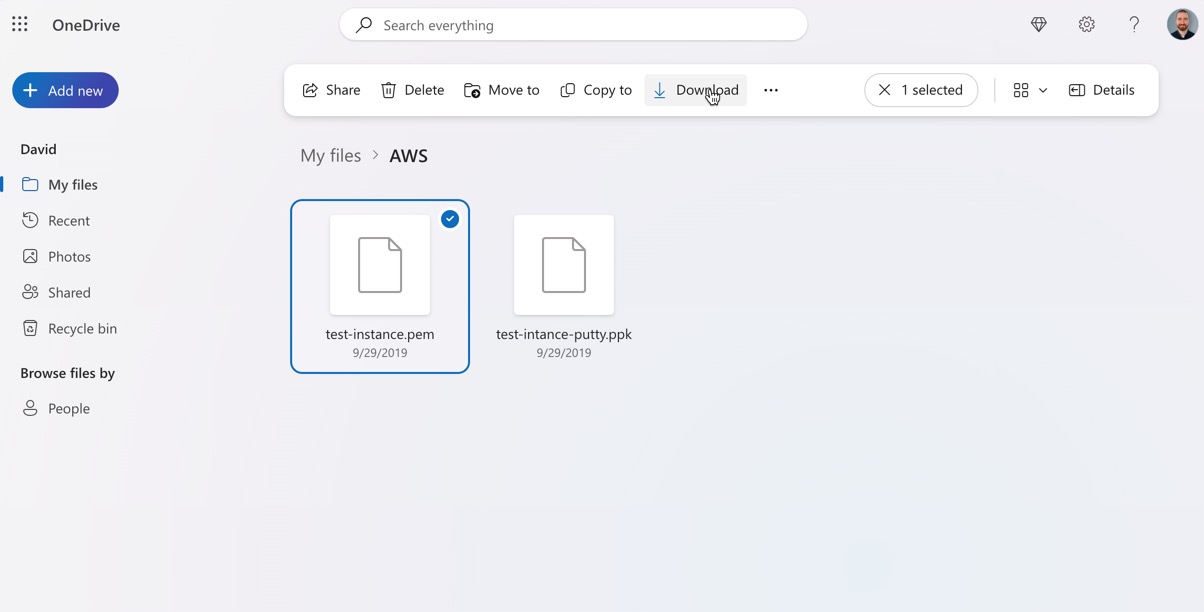
- Log in to your OneDrive account on a different device or through the web.
- Locate the files or folders you want to recover and select them.
- Click the Download button to save the files to the new device.
File History:
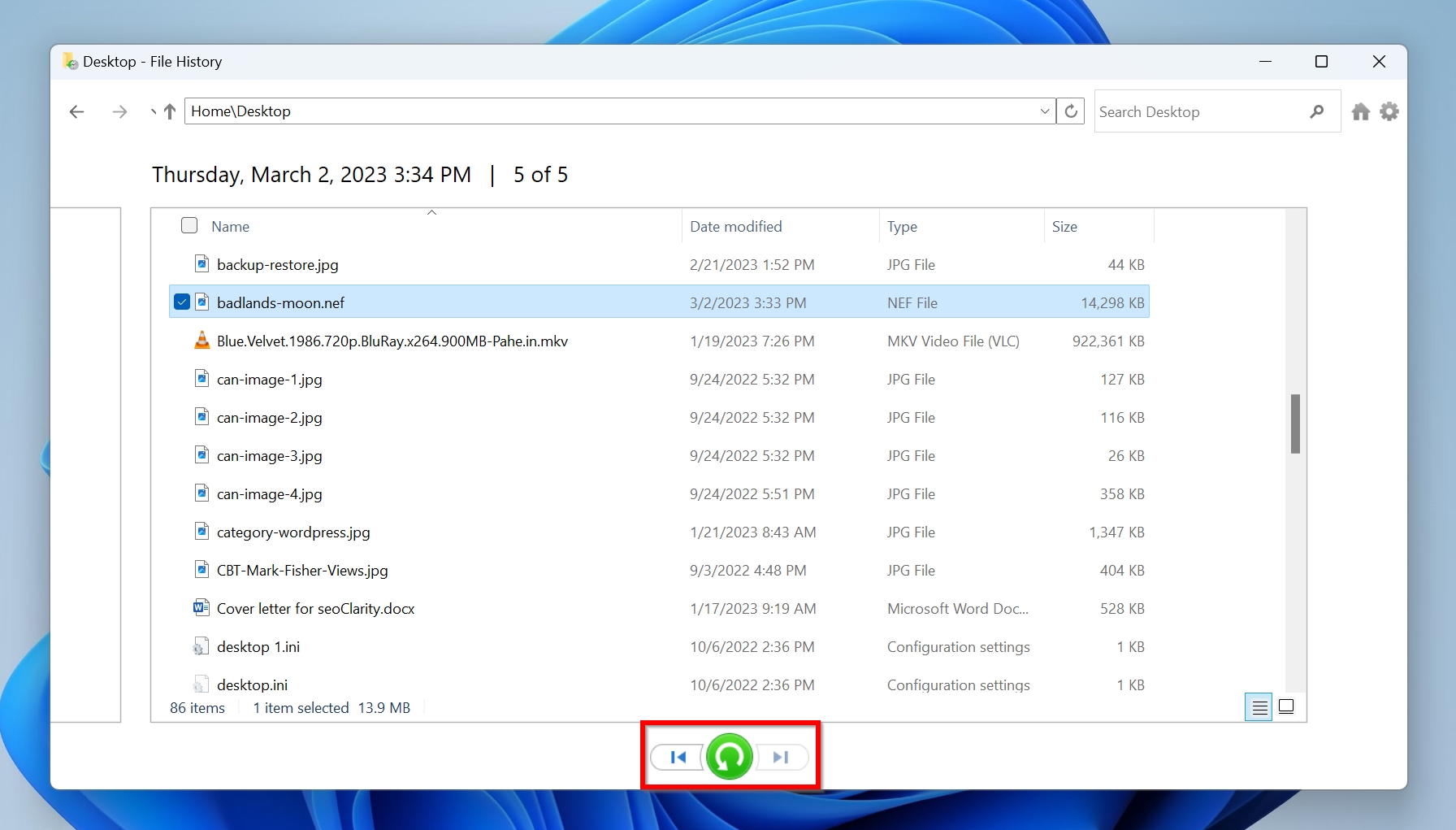
- Connect the drive containing the File History backup to your computer.
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > File History. Your existing backup drive should be automatically detected.
- Click Restore personal files and select the files or folders you want to recover.
- Click the green Restore button to complete the recovery process.
Manual Backups:
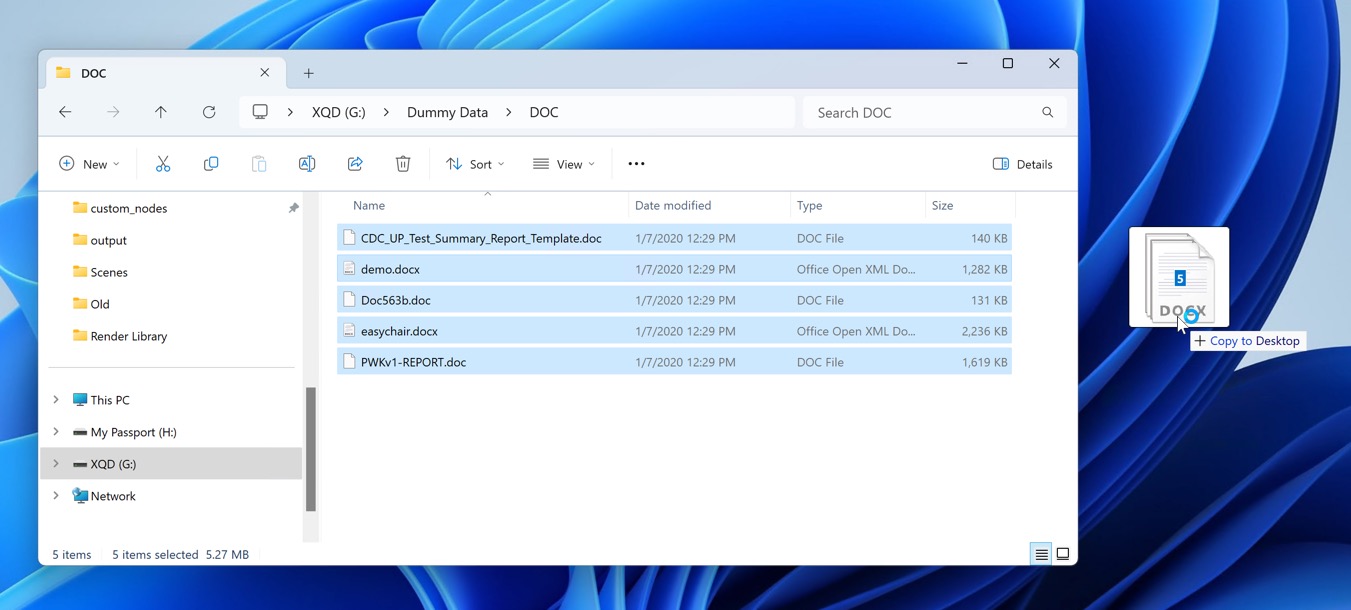
- Connect the backup drive or device to your computer.
- Locate the files or folders you want to recover.
- Copy them to the new device or hard drive.
Option 2: Use Data Recovery Software
When it comes to recovering data from a wiped hard drive using data recovery software, the solution we recommend the most is Disk Drill.
Disk Drill stands out with its user-friendly interface and powerful recovery capabilities that make it possible even for regular Windows users to achieve professional results. The software can identify and recover wiped data based on available file system information (this makes it possible to recover metadata) and signatures (enables the recovery of completely wiped drives).
All major Windows file systems, including NTFS, FAT, FAT32, and exFAT are fully supported, and so are macOS and Linux file systems. Included with Disk Drill are several extra features that can help you recover a wiped hard drive, including a S.M.A.R.T. monitoring tool and a byte-to-byte backup feature.
Follow the steps below to recover a wiped non-system hard drive using Disk Drill. If the wiped hard drive is a system drive, skip to the subsection below for additional instructions and then come back to these instructions.
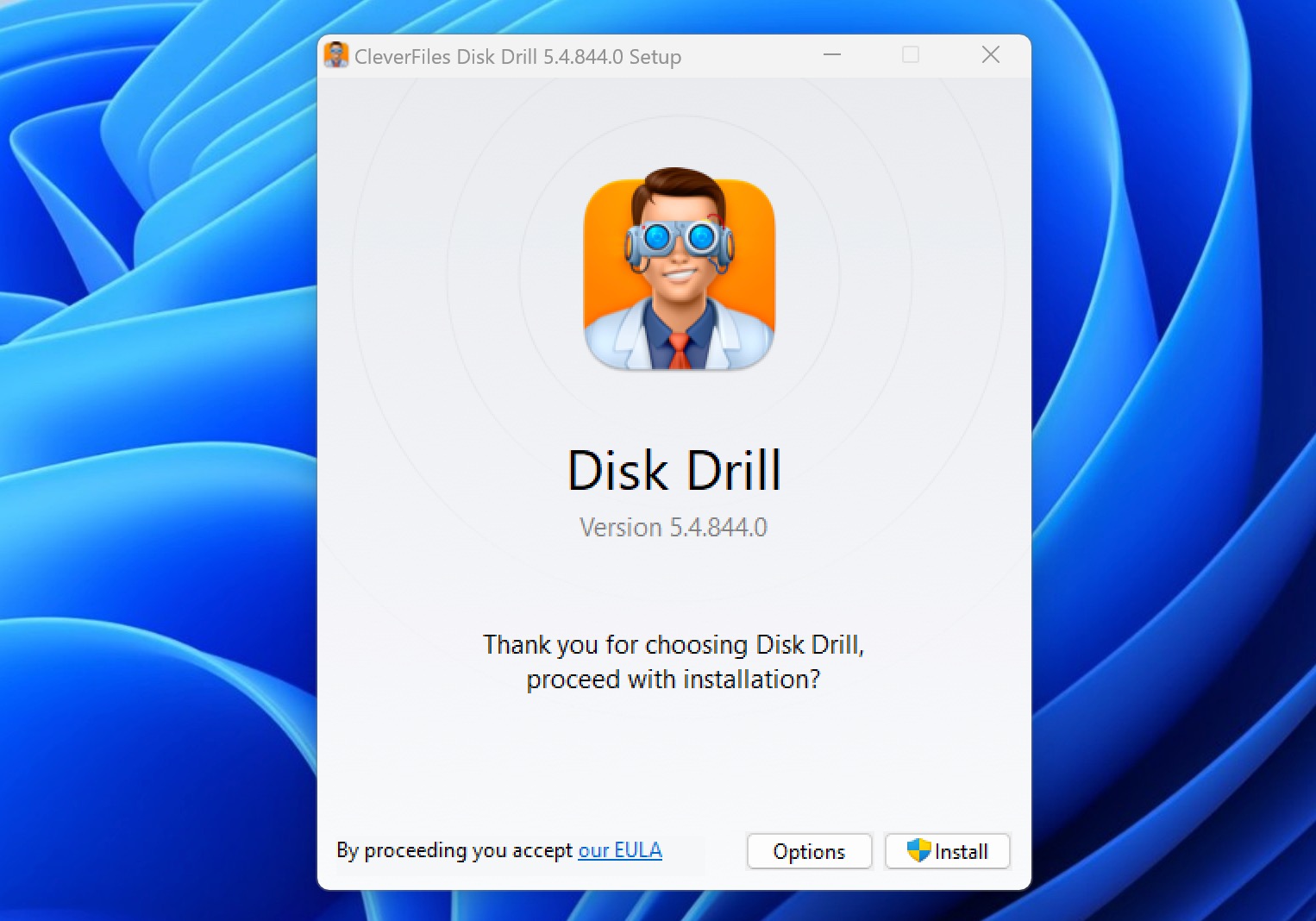
- Visit the Disk Drill website to download the installer. Run the setup file and follow the installation prompts to install Disk Drill on your Windows computer.
- Open Disk Drill. The main window will display a list of all storage devices connected to your computer. Identify the wiped hard drive from the list and select it by clicking on its icon.
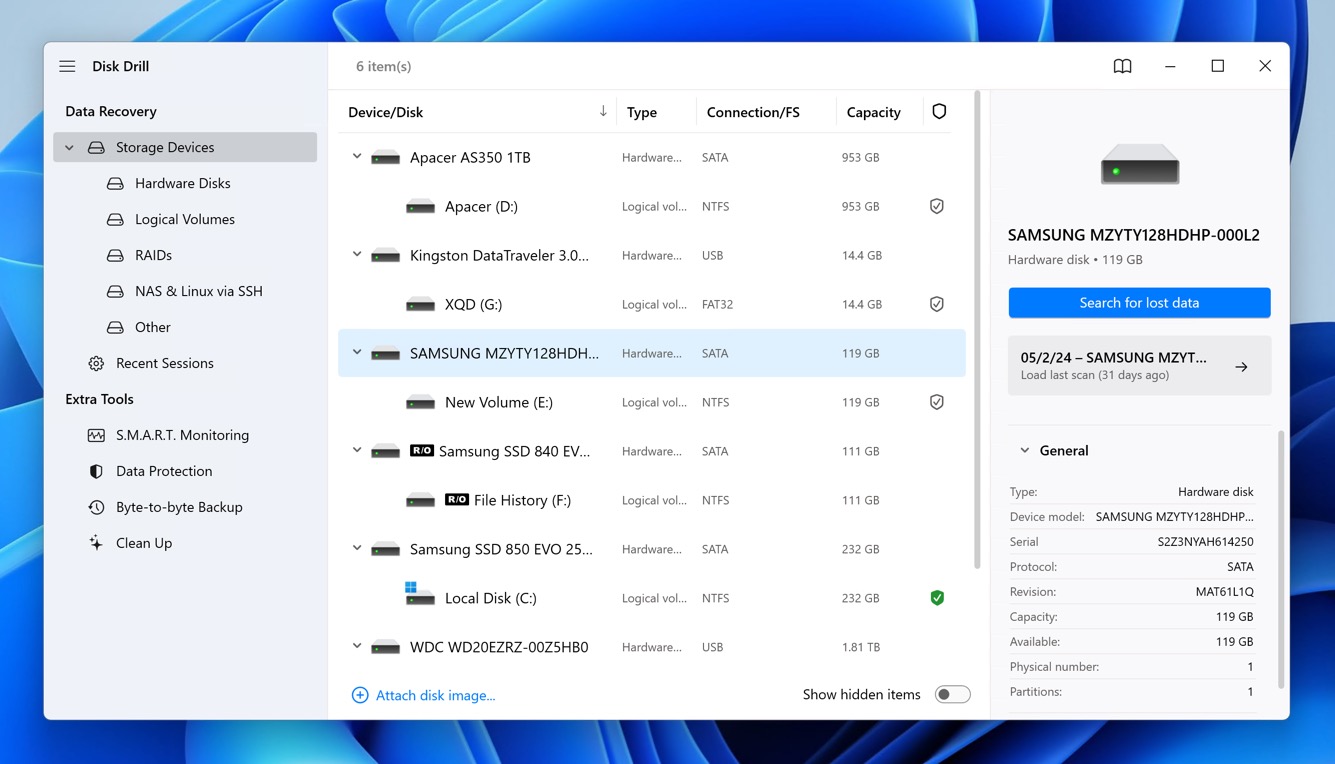
- With the drive selected, click on the Search for lost data button. Disk Drill will start scanning the drive, looking for recoverable files. This process can take some time, so be patient.
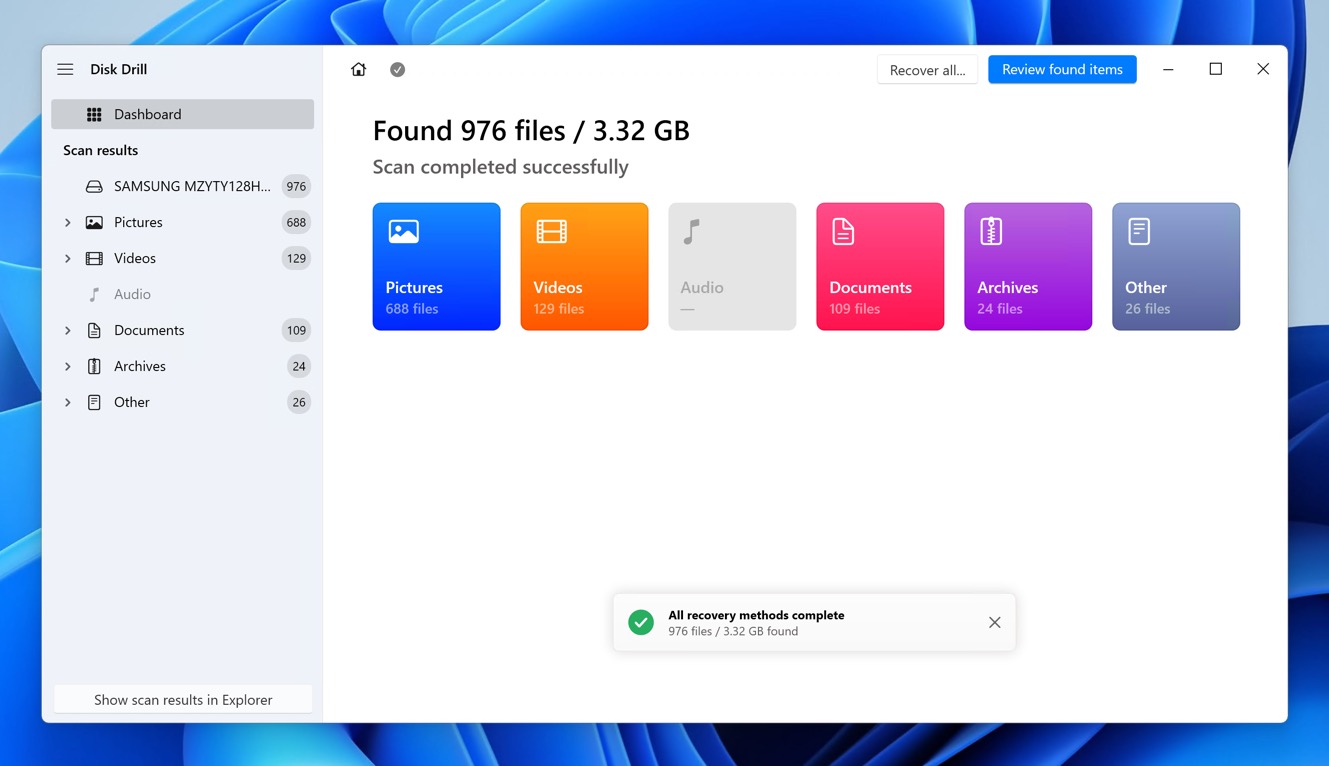
- Once the scan is complete, Disk Drill will display the recoverable files. You can apply various filters and use the preview function to view files before recovery, which helps in identifying the files you need. Click the checkbox next to each file you want to recover.
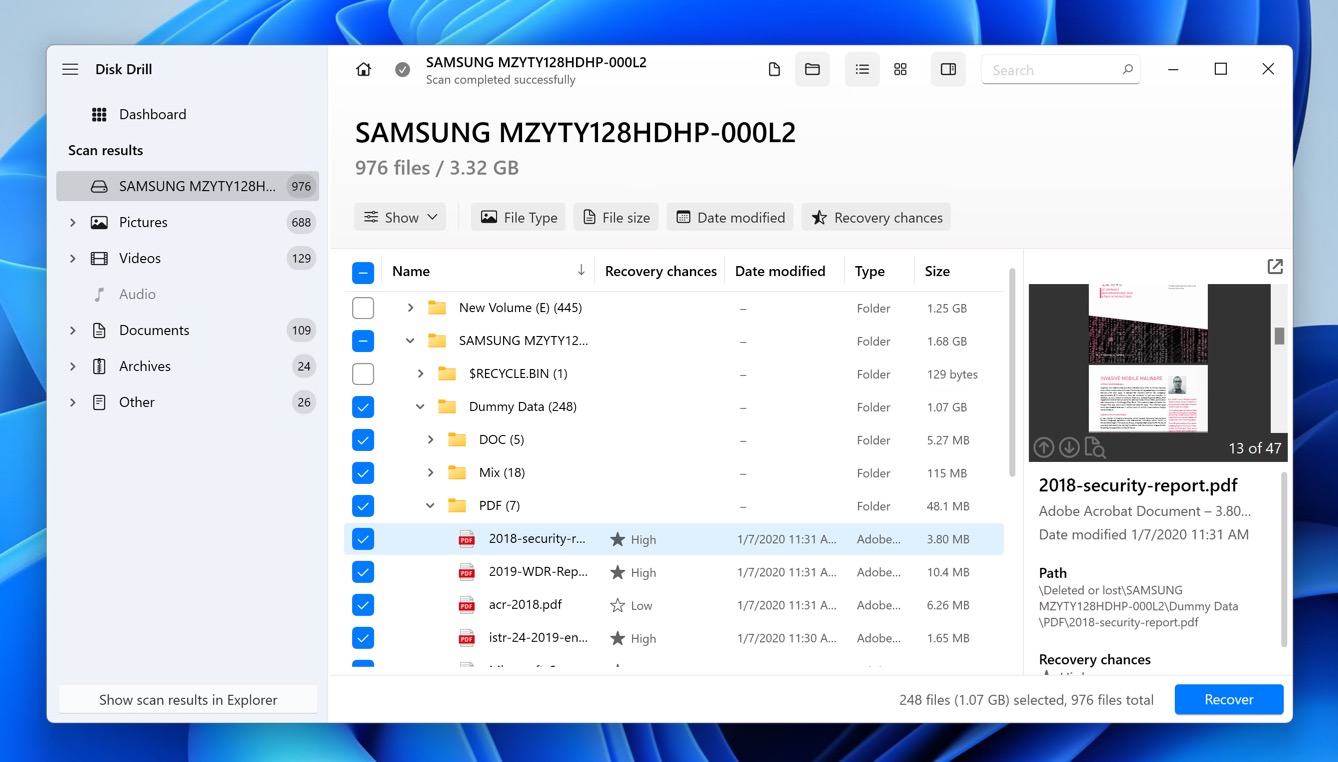
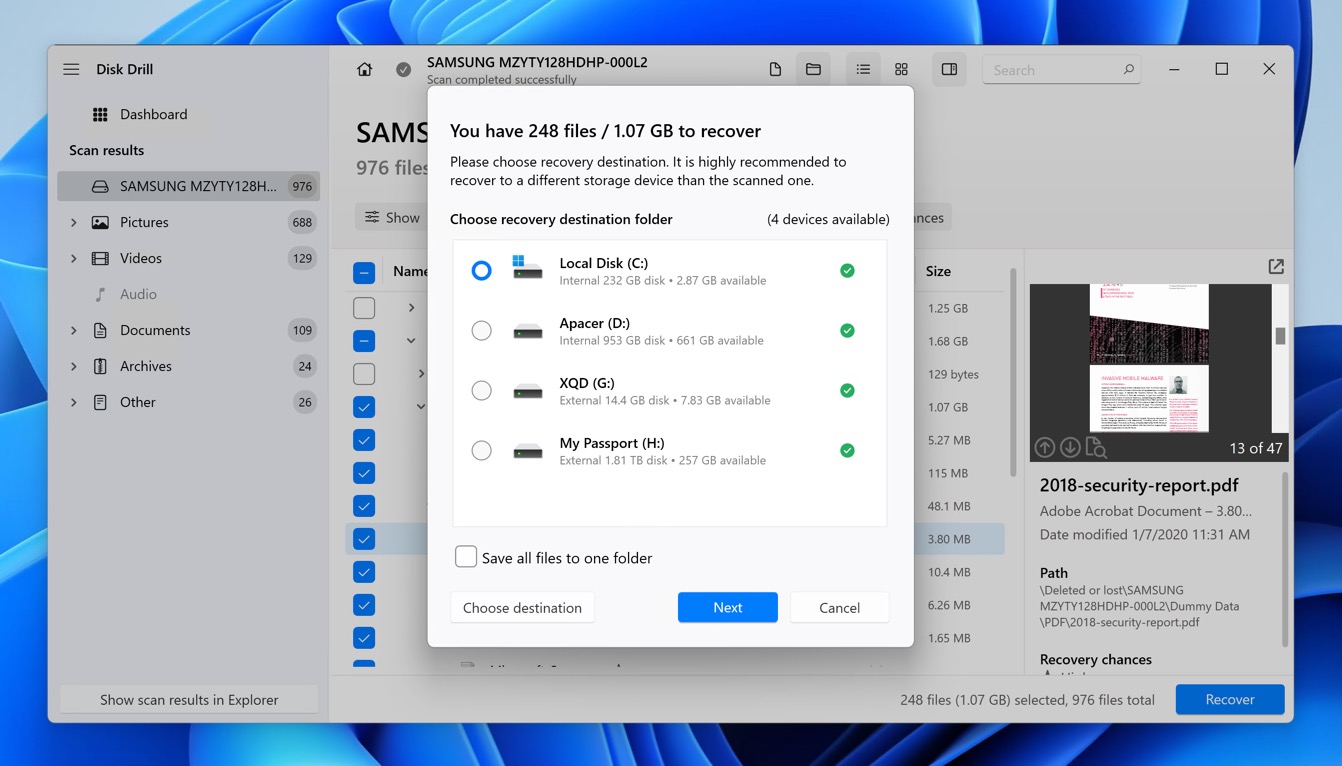
- After selecting the files you wish to recover, click on the Recover button. Choose a safe location to save the recovered files. It’s recommended to save the files to a different drive than the one you are recovering from to prevent overwriting any data.
Recover a System Drive With Data Recovery Software
It’s possible that the wiped hard drive or partition contained the Windows OS. Therefore, you cannot perform data recovery on the same computer that houses the HDD as the computer won’t boot. In this case, you will need another computer to perform data recovery using data recovery programs.
Instructions on how to connect a wiped hard drive to another PC and recover data from it:
- Remove the HDD from the original PC. This process will differ across manufacturers, but there are various YouTube videos that can familiarize you with the process. Don’t forget to refer to your motherboard and PC cabinet’s user manuals as well
- Now, you’ll need to purchase a hard drive enclosure and place the wiped hard drive inside the enclosure. Remember to connect the relevant cables by using the manual.

- Lastly, connect the enclosure to the PC using its USB cable. After connecting the hard drive, your PC should detect the hard drive as any other storage drive. You can then use Disk Drill to scan the drive and recover your lost data.
Option 3: Pay a Professional Data Recovery Service

If the hard drive was wiped because of physical damage, it’s better to contact a data recovery service. While you can recover data from a corrupted hard drive in some cases, severe logical corruption that renders the HDD unreadable is best dealt with by professional services.
Data recovery services are substantially more expensive than data recovery programs, but your drive is handled by experts.
An overview of how data recovery services operate:
- The user contacts the data recovery company and books an evaluation.
- The wiped hard drive needs to be dropped off or shipped to the data recovery lab.
- The company evaluates the drive (usually free).
- If there is recoverable data, the company contacts the user and provides them with a quote.
- The user can then decide if they want to proceed with the data recovery.
What Happens When a Hard Drive Is Wiped
There are different reasons why a hard drive could be completely wiped. What exactly happens in some common scenarios is explained below:
| Reason for a Wiped Hard Drive | Explanation |
| The user accidentally deletes all the data. | In this case, the files are still on the drive, but they’re marked as invisible. Therefore, until new data overwrites the previous data, you can still restore your files. |
| The user formats the drive. | A Full Format is irreversible and permanently erases the data. However, you can still recover data after a Quick Format. |
| The hard drive is wiped because of logical damage. | Mild logical damage due to malware or corruption can cause data loss, which can be easily undone using data recovery software. Severe logical damage is harder to deal with, and a data recovery service is your only bet. |
| Physical damage such as shock, a power surge, or water, damages the hard drive and makes the data inaccessible. | Physical damage cannot be handled at home, and attempting DIY recovery will further harm the wiped hard drive. Again, it’s best to contact a professional data recovery service. |
| The hard drive was wiped using shredding programs. | There are specialized programs that are created for wiping out hard drives. HDDs wiped using these apps are impossible to recover data from. |
Conclusion
Contrary to how it may seem at first, it’s often possible to recover data from a wiped hard drive. This article has outlined three primary methods: restoring from an available backup, using data recovery software like Disk Drill, and seeking professional data recovery services for severe cases. We hope that by following these steps, you can successfully retrieve your valuable data and mitigate the impact of accidental data loss.













